How to Find the Solution Set of a Rational Inequality
Solving Rational Inequalities
The key approach in solving rational inequalities relies on finding the critical values of the rational expression which divide the number line into distinct open intervals.
The critical values are simply the zeros of both the numerator and the denominator. You must remember that the zeros of the denominator make the rational expression undefined, so they must be immediately disregarded or excluded as a possible solution. However, zeros of the numerator also need to be checked for its possible inclusion to the overall solution.
In this lesson, I will go over five (5) worked examples with varying levels of difficulty to illustrate both the procedures and concepts.
Examples of How to Solve Rational Inequalities
Example 1: Solve the rational inequality below.
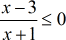
I begin solving this rational inequality by writing it in general form. The general form implies that the rational expression is located on the left side of the inequality while the zero stays on the right.
The general form has four (4) types.
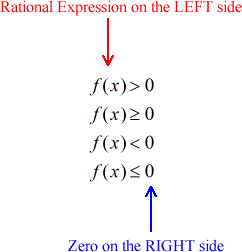
It's good to know that this problem is already in the general form. My next step is to find the zeros of both numerator and denominator.
I can find the zeros of the numerator by factoring it out completely and then separately set each factor equal to zero and solve for x. Likewise, finding the zeros of the denominator is done the same way.
- Zeros of numerator
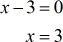
- Zeros of denominator
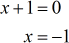
Now, I will use the zeros to separate or partition the number line into intervals. The zeros of the numerator and denominator are also known as the critical numbers. In this case, the two critical numbers divide the number line into three distinct intervals.
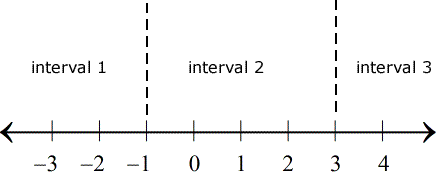
The next step is to pick or select a number in every interval and evaluate it back into the original rational inequality; to determine if it is a true or false statement. A true statement means that an interval is part of the solution, otherwise, it is not.
As you can see, the numbers I picked for each interval are highlighted in yellow.
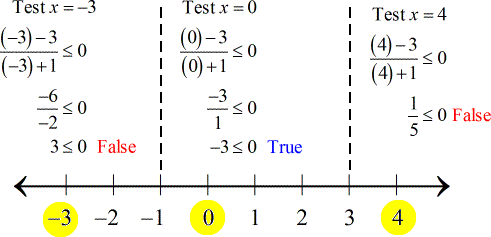
Notice that the open interval between −1 and 3, written as \left( { - 1,3} \right), yields a true statement which implies that it is part of the solution.
So, where else do we look for possible solutions to finish this off?
Check the zeros or critical numbers of the numerators only into the original equation. If it gives a true statement then include that critical number as part of the overall solution.
The zeros of the numerator is 3. Now I will verify it.
![[(3-3)/(3+1)] is less than or equal to 0 results to 0 is less than or equal to 0 which is a true statement.](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex1_checkcn.gif)
The use of a square bracket indicates that it is part of the solution, while an open bracket (parenthesis) denotes that it's not. I will write my final answer as \left( { - 1,\left. 3 \right]} \right..
Example 2: Solve the rational inequality below.
![[(x^2+2x-8)/(x+2)] is greater than 0](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex2-11.gif)
First off, the given rational inequality is in general form because the rational expression is on the left while the zero is on the right side. That's good!
Next, I will factor out the numerator and the denominator. After doing so, you should have something like this.
![{[(x+2)(x+4)]/(x+2)} is greater than 0](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex2_factored.gif)
I can now find the zeros of the numerator and denominator.
- Zeros of numerator
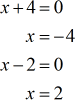
- Zeros of denominator
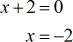
These zeros or critical numbers divide the number line into distinct intervals or partitions.
Select a test number for each interval and substitute back to the original rational inequality.
Use the factored form of the original rational inequality to evaluate test numbers for ease of calculation.
The numbers in yellow are the ones I chose to test the validity of each interval.
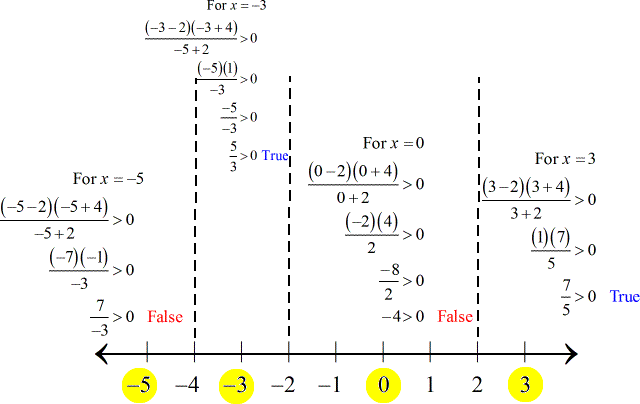
The intervals yielding true statements are
To find the rest of the solution, check the validity of the zeros of the numerator only into the original rational inequality.
If you have done it correctly, you should agree that −4 and 2 are not valid answers because they don't give true statements after checking.
The final answer to this problem in interval notation is
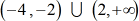
Example 3: Solve the rational inequality below.
![[(x^2-3x-4)/(x62-8x+16)] is less than 0](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex3-11.gif)
I would factor out the numerator and denominator first to find their zeros. In factored form, I got
![{[(x+1)(x-4)]/[(x-4)(x-4)]} is less than 0](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex3_factored.gif)
Next, determine the zeros of the rational inequality by setting each factor equal to zero then solving for x.
- Zeros of the numerator:–1 and 4
- Zeros of the denominator: 4
Use the zeros as critical numbers to divide the number line into distinct intervals. I start testing the validity of each interval by selecting test value and evaluating them into the original rational inequality. The ones in yellow are the numbers I picked.
Notice that the only interval giving a true statement is \left( { - 1,4} \right).
More so, the zeros of the numerator don't check with the original rational inequality so I must disregard them.
The final answer is just \left( { - 1,4} \right).
Example 4: Solve the rational inequality below.
![[(2x+10)/(x+3)] is greater than or equal to 1](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex4-9.gif)
This rational inequality is not in general form. The right-hand side must be zero. The first step is to get rid of the constant on that side by subtracting both sides by 1. After that, simplify into a single rational expression. You should have a similar preliminary step just like this.
![[(x+7)/(x+3)] is greater than or equal to 0.](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex4_transform.gif)
Next, find the zeros of the numerator and denominator.
- Zeros of the numerator:-7
- Zeros of the denominator:-3
Use the zeros as critical numbers to partition the number line into sections or intervals.
Then pick test numbers for each interval and evaluate them into the general form to determine their truth values. The ones in yellow are the selected values. You may choose other numbers as long as they are in the interval being tested.
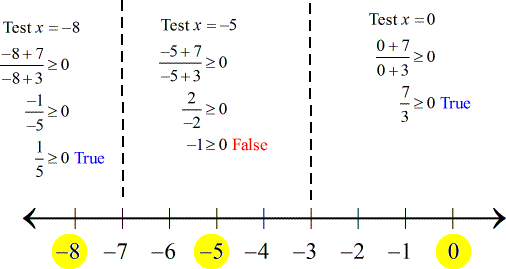
The intervals giving true statements are
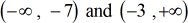
Meanwhile, after checking the zero of the numerator at x = - \,7, it also results in a true statement. Use the square bracket for that to indicate it's being included as a solution.
The final answer in interval notation should be
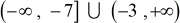
Example 5: Solve the rational inequality below.
![[(3x-15)/x] less than or equal to (5-x)](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex5-8.gif)
I need to make the right side of the rational inequality zero. To do that, I will simultaneously add x and subtract 5 on both sides. However, my ultimate goal is to express it in a single rational expression. This is where your skills on how to add and subtract rational expressions will be useful. You should have similar steps below.
![[(x-5)(x+3)]/x is less than 0](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex5_transform.gif)
Next, find the zeros of the numerator and denominator.
- Zeros of the numerator:-3 and 5
- Zeros of the denominator: 0
Make use of the zeros to divide the number line into distinct intervals. Choose test numbers for each interval to check if it results in true statements. The selected test values for x are in yellow.
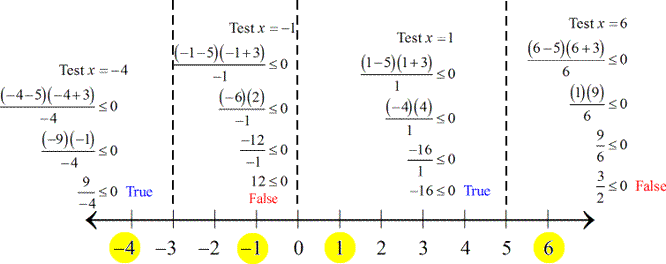
The "true" intervals are \left( { - \,\infty , - 3} \right) and \left( {0,5} \right). More so, the zeros of the numerator also check with the general form of the given rational inequality. Consequently, I have to include -3 and 5 as part of the solution with the use of square brackets.
The final answer now becomes
![(negative infinity, -3] union (0, 5]](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/ex5_final.gif)
Practice with Worksheets
You might also be interested in:
Solving Rational Equations
Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
Multiplying Rational Expressions
How to Find the Solution Set of a Rational Inequality
Source: https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/advanced-algebra/solving-rational-inequalities/